Living with diabetes and effectively managing blood glucose levels is a daily challenge for millions of individuals worldwide. However, in recent years, a breakthrough in diabetes technology has emerged, transforming how people manage their condition. Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) have become true game-changers, offering real-time data and empowering individuals to take control of their diabetes management like never before.
In this blog post, we will delve into the fascinating world of CGMs and explore how these innovative devices are revolutionizing diabetes technology in 2023.
From advancements in accuracy and user-friendliness to enhanced safety features and improved quality of life, CGMs have ushered in a new era of diabetes management. We will delve into the benefits of CGMs, including their ability to provide real-time data for optimal management and their role in reducing the frequency and severity of hypoglycemic events.
At Aptiva Medical, we recognize the significance of CGMs in diabetes care and the transformative impact they have on the lives of individuals who use insulin. Our commitment to empowering individuals and advancing diabetes technology drives us to stay at the forefront of this revolution, ensuring that our patients have access to the most innovative and effective solutions available.
Understanding Different Types of Diabetes Tests
When it comes to managing diabetes, regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is crucial. Several types of diabetes tests are available, each serving a specific purpose in assessing and managing diabetes. Understanding these tests can help individuals make informed decisions about their diabetes management and ensure they receive the appropriate care.
Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG)
SMBG involves regularly checking blood glucose levels at home using a glucose meter and test strips. It provides immediate feedback on glucose levels and is an essential tool for day-to-day diabetes management. SMBG allows individuals to make informed decisions regarding insulin doses, medication adjustments, meal planning, and physical activity (Diabetes Journals, 2023). This method of self-monitoring empowers individuals to take an active role in managing their diabetes and maintaining optimal glycemic control.
For a detailed understanding of SMBG, you can refer to the research study titled “Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose: The Basics.” This study offers valuable insights into the fundamentals of SMBG and its role in diabetes management.
Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) Test
This test measures blood glucose levels after an overnight fast of at least 8 hours. It is commonly used to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes. A fasting plasma glucose level of 100-125 mg/dL indicates prediabetes, while a level of 126 mg/dL or higher on two separate occasions confirms a diagnosis of diabetes. To gain a deeper understanding of the Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) test, you can read the article “Understanding the Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) Test.”

Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
The OGTT involves drinking a glucose solution followed by blood glucose measurements at specific time intervals. It is used to diagnose gestational diabetes, prediabetes, and diabetes. If you are wondering if you need an oral glucose tolerance test, it is best to consult with your healthcare provider. They will consider your medical history, risk factors, and symptoms to determine if an OGTT is necessary in your specific case. After fasting, a blood sample is taken, and then the glucose solution is consumed. Blood samples are taken again at specific intervals (typically 1 hour, 2 hours, and sometimes 3 hours) to assess how the body processes glucose. Elevated glucose levels at any point during the test can indicate impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes.
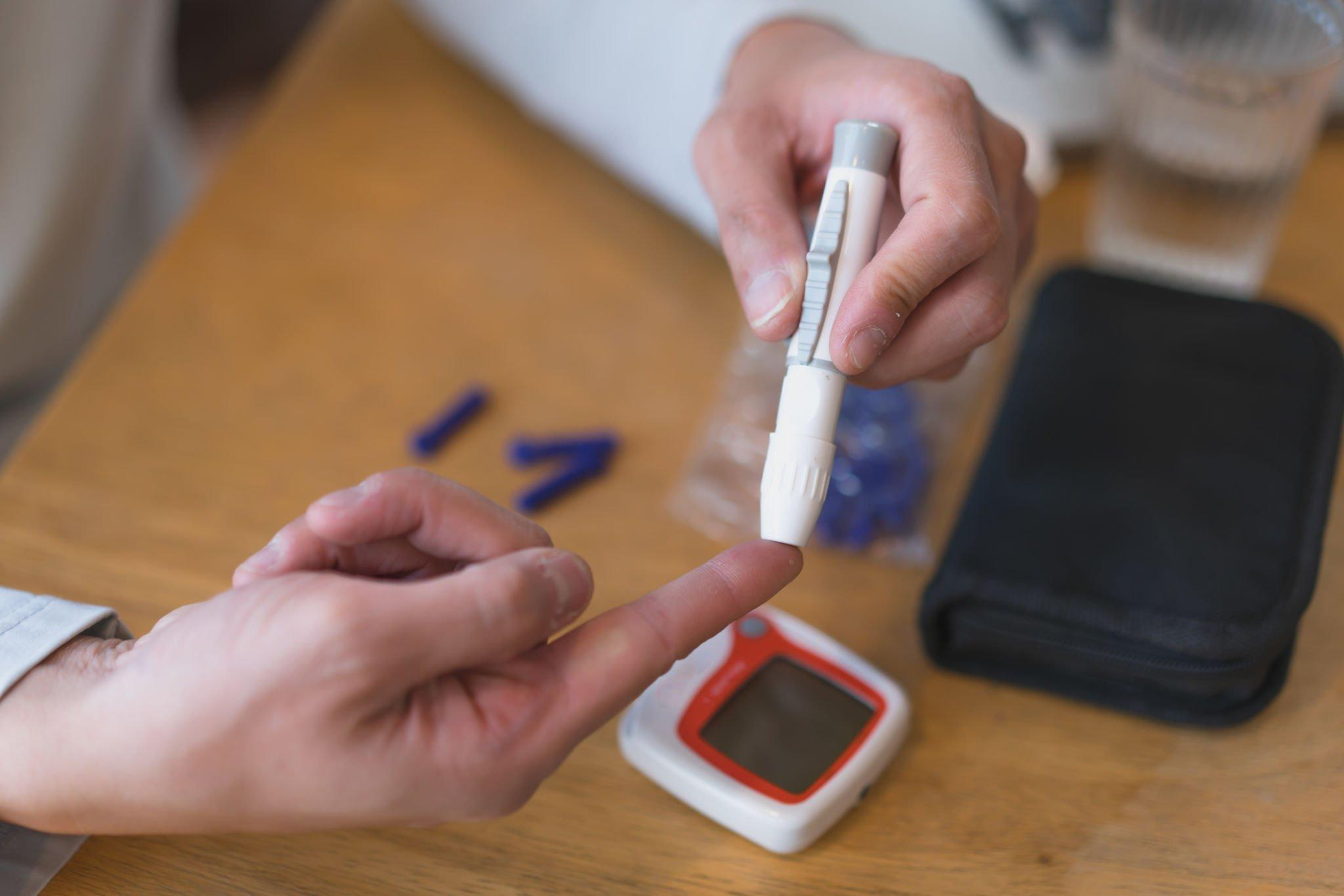

Random Plasma Glucose Test
This test involves checking blood glucose levels at any time of the day, regardless of the time since the last meal. It is often used to diagnose diabetes when symptoms are present, such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, or unexplained weight loss. A random plasma glucose level of 200 mg/dL or higher, along with diabetes symptoms, may indicate diabetes.

Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) Test
The HbA1c test provides an average measure of blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months. It is commonly used to monitor long-term glycemic control in individuals with diabetes. The test reflects the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that has glucose attached to it. A result of 5.7% to 6.4% indicates prediabetes, while a result of 6.5% or higher on two separate occasions confirms a diagnosis of diabetes.
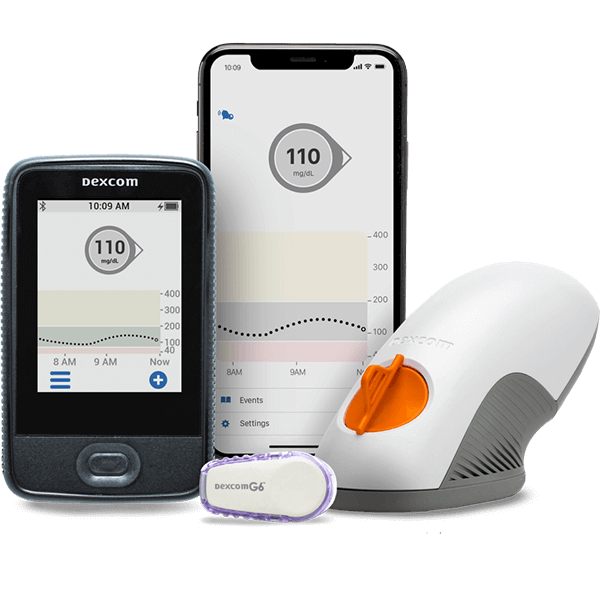
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
CGM is a method of diabetes testing that involves wearing a device that continuously measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. It provides real-time data and trend analysis, allowing individuals to monitor their glucose levels throughout the day and night. CGM is particularly beneficial for individuals who require frequent monitoring or those who experience hypoglycemic events. It offers insights into glucose patterns, helps identify trends, and facilitates informed diabetes management decisions.
It is important to note that the choice of diabetes test depends on various factors, including the individual’s specific needs, the stage of diabetes management, and healthcare provider recommendations. Some individuals may require multiple types of tests to gain a comprehensive understanding of their glucose levels and make informed decisions about their diabetes care.

The Rise of Continuous Glucose Monitors
In recent years, continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) have experienced a remarkable rise in popularity and adoption within the field of diabetes management. These innovative devices have emerged as a game-changer, replacing the traditional fingerstick method and providing individuals with a convenient and continuous way to monitor their blood glucose levels.
One of the key factors driving the rise of CGMs is the advancement in sensor technology. CGMs now utilize small, flexible sensors that are inserted under the skin to measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. These sensors have become more accurate, reliable, and comfortable, making them a preferred choice for many individuals managing their diabetes.
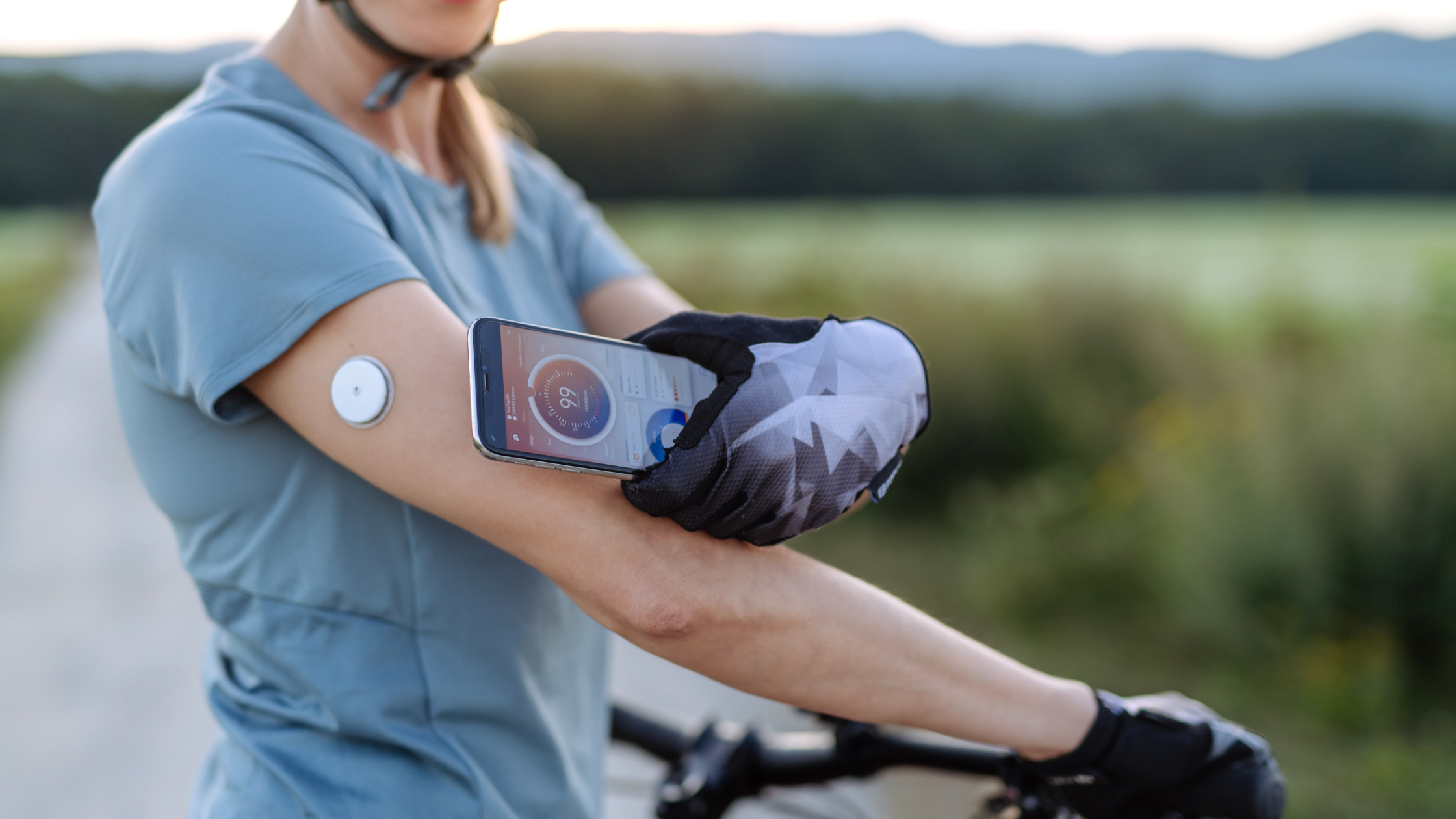
Furthermore, CGMs have become increasingly user-friendly, with intuitive interfaces and seamless integration with various digital platforms. Many CGMs allow users to easily access their glucose data through smartphone apps, smartwatches, or dedicated receiver devices. This accessibility not only provides convenience but also encourages individuals to actively engage with their glucose data and make informed decisions regarding their diabetes management.
The popularity of CGMs can also be attributed to the growing recognition of the limitations of traditional glucose monitoring methods. Fingerstick testing, while effective, only provides a snapshot of blood glucose levels at a specific moment. CGMs, on the other hand, offer continuous and real-time data, allowing users to observe glucose trends, identify patterns, and detect fluctuations that might otherwise go unnoticed. This valuable information empowers individuals to adjust their insulin doses, modify their dietary choices, and make proactive decisions to optimize their glucose control.
Moreover, the benefits of CGMs extend beyond individuals with type 1 diabetes. They have also proven to be highly valuable for individuals with type 2 diabetes who require insulin therapy or those who want to closely monitor their glucose levels for better management and overall well-being.
The rise in CGM adoption is not only driven by the benefits they offer to individuals but also by the growing support and advocacy from healthcare professionals and diabetes organizations. As the evidence supporting the effectiveness and benefits of CGMs continues to accumulate, healthcare providers are increasingly recommending CGMs as a standard tool for diabetes management.
Real-Time Data for Optimal Management
One of the most significant advancements offered by continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) is the provision of real-time data for optimal diabetes management.

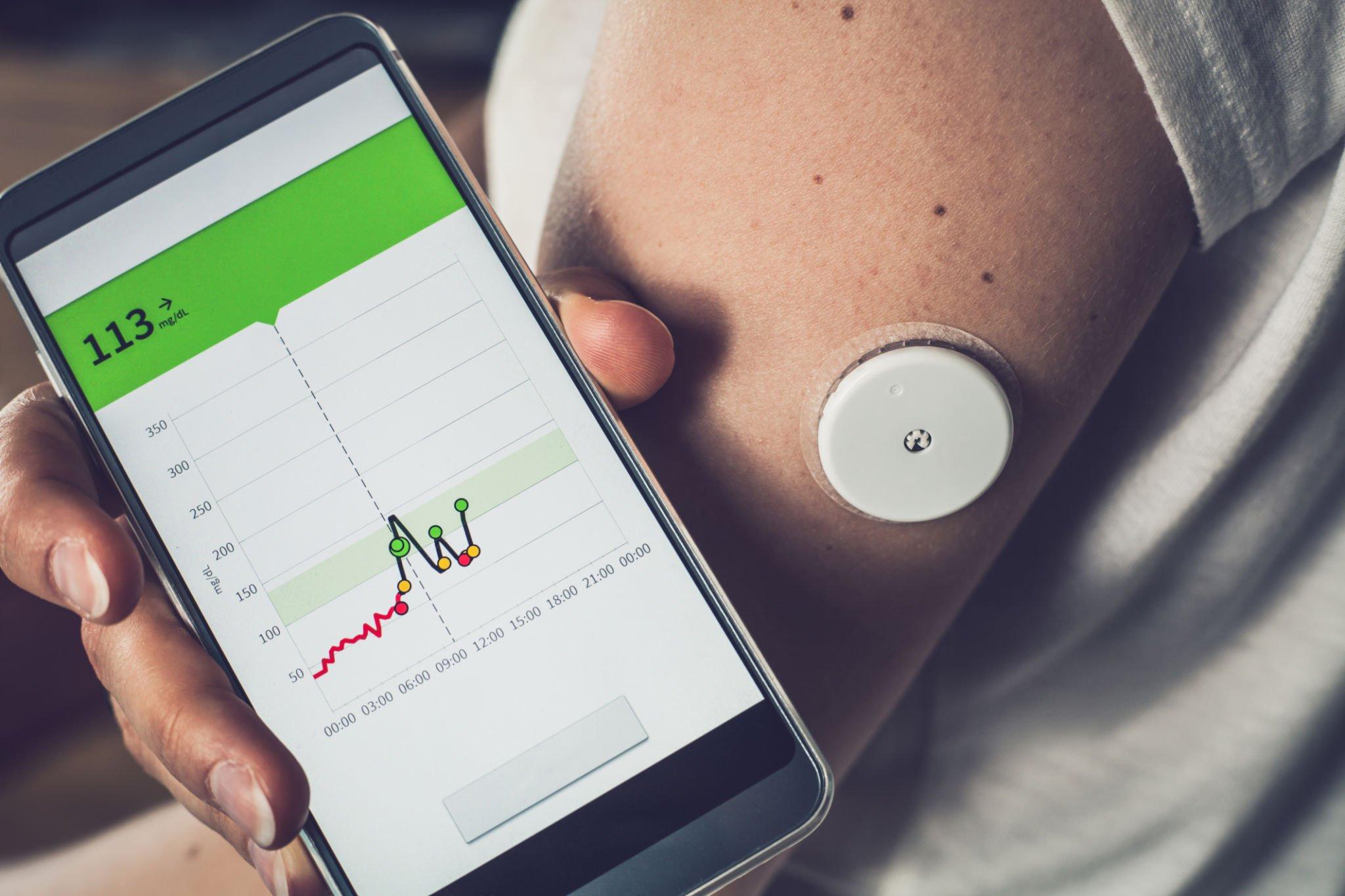
Tracking of glucose level over time
With traditional fingerstick testing, individuals could only obtain isolated snapshots of their glucose levels at specific moments. However, CGMs offer a continuous stream of data, allowing users to track their glucose patterns over time. This real-time information provides valuable insights into how the body responds to various factors such as meals, physical activity, medication, and stress.
By having access to real-time data, individuals can make informed decisions about their diabetes management. They can observe the impact of different foods and make dietary adjustments accordingly. They can also assess the effects of exercise and adjust insulin doses or carbohydrate intake as needed to maintain stable glucose levels. This ability to respond promptly to changing glucose levels empowers individuals to achieve better glycemic control and reduce the risk of hypo- and hyperglycemic episodes.
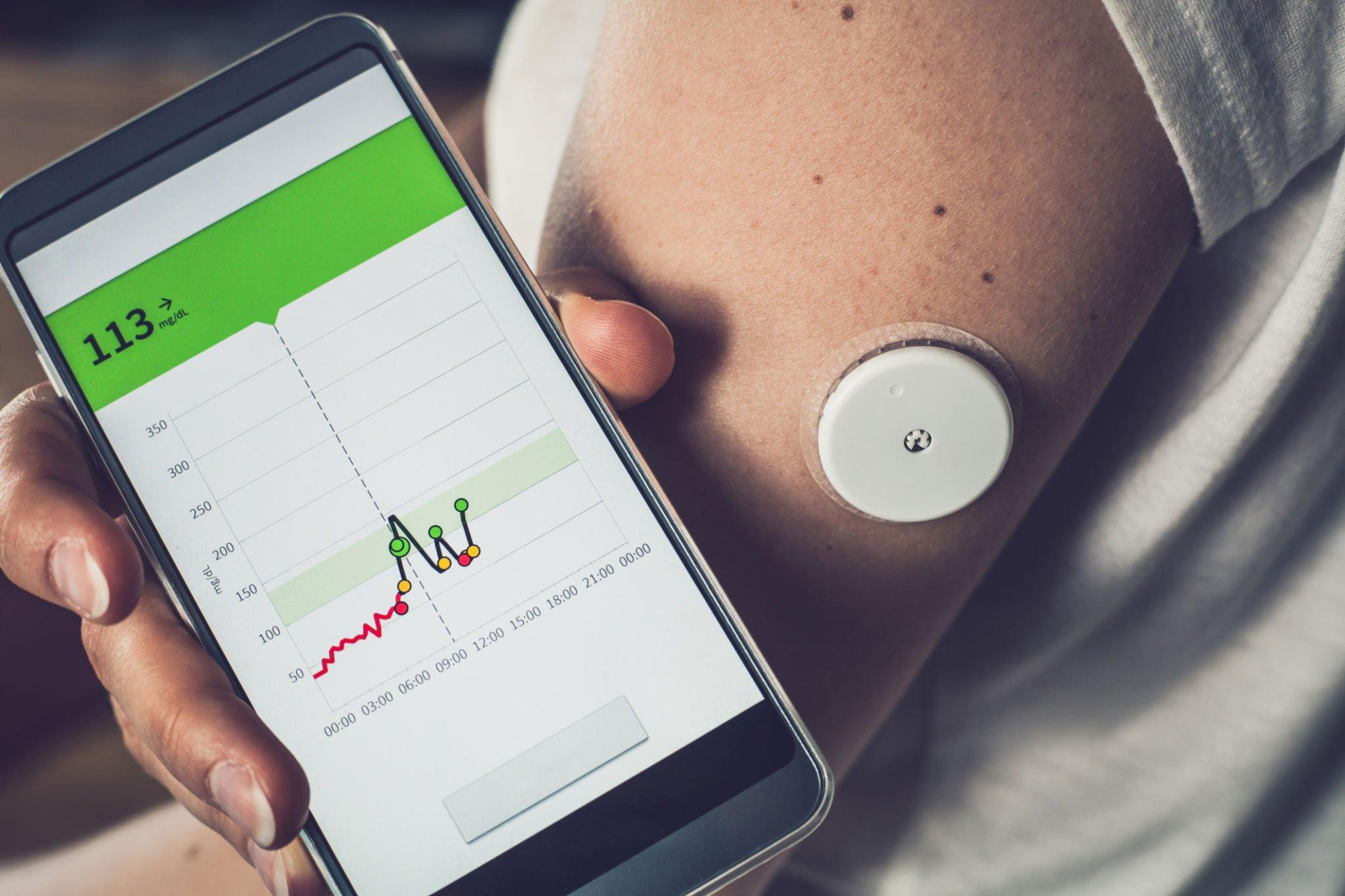

Detect glucose trends and patterns
Another key advantage of real-time CGM data is the ability to detect glucose trends and patterns. CGMs display glucose trends through intuitive graphs and visualizations, allowing users to identify patterns such as post-meal spikes, overnight fluctuations, and recurring hypoglycemic episodes. This information enables individuals and their healthcare providers to optimize insulin therapy, make targeted lifestyle modifications, and create personalized diabetes management plans.
Furthermore, CGMs often provide customizable alerts and alarms to notify users when their glucose levels fall outside a predetermined target range. These alerts act as a safety net, allowing individuals to take immediate action to prevent hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic events. This feature is particularly crucial for individuals who may have impaired hypoglycemia awareness or are at a higher risk of severe glucose fluctuations.
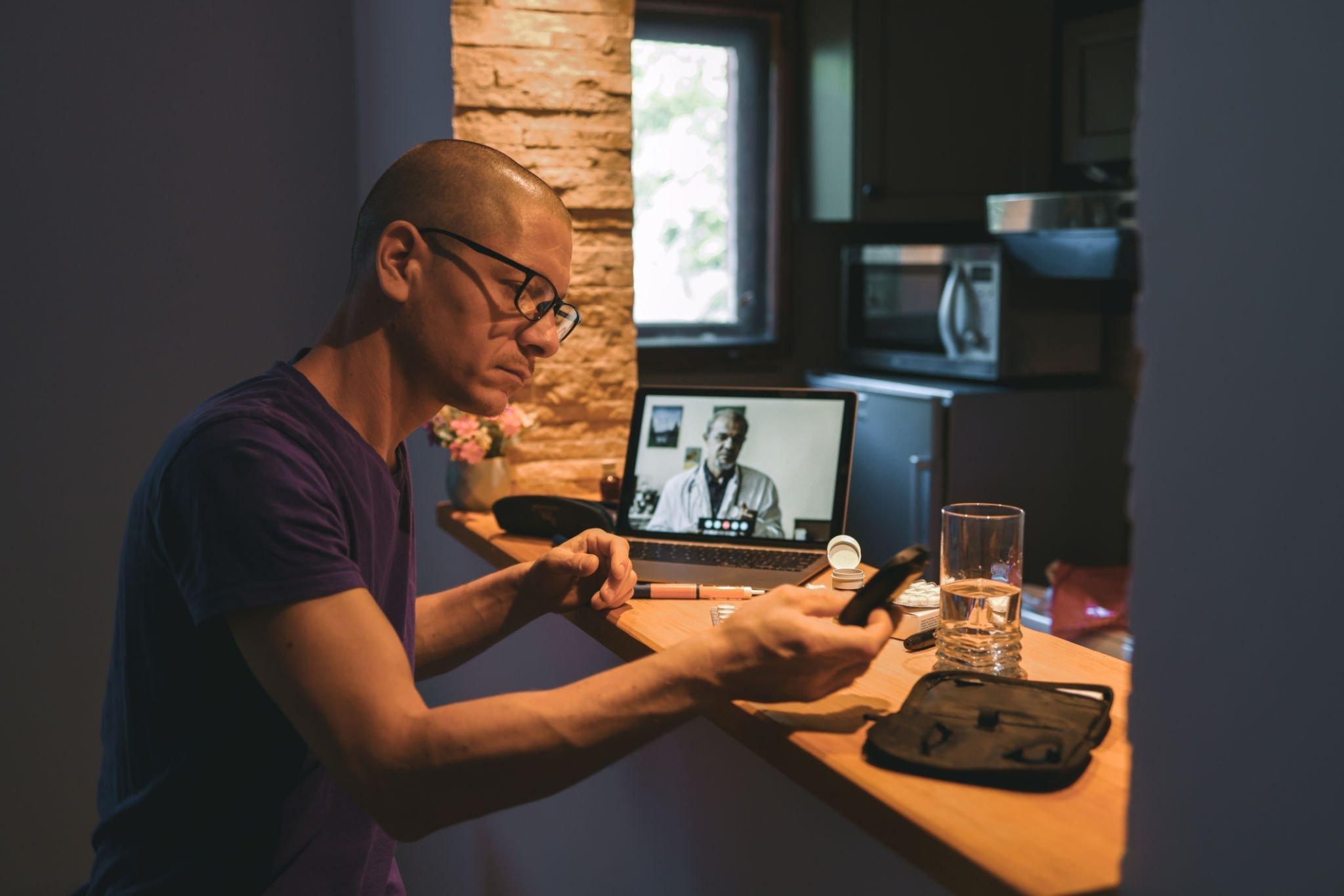

Easily share your glucose data
The availability of real-time data from CGMs also facilitates data sharing between individuals and their healthcare providers. Through secure digital platforms, users can conveniently share their glucose data with their healthcare team, who can then analyze the information and provide tailored recommendations for improved diabetes management. This collaborative approach ensures that individuals receive personalized and evidence-based guidance, leading to more effective treatment plans and better overall outcomes.
The real-time data provided by CGMs has revolutionized diabetes management by empowering individuals with continuous feedback on their glucose levels. The ability to track glucose patterns, make timely adjustments, and share data with healthcare providers has transformed the way individuals optimize their diabetes management.

Enhanced Safety and Fewer Hypoglycemic Events
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) have played a pivotal role in enhancing the safety of individuals managing diabetes by significantly reducing the occurrence and severity of hypoglycemic events. Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, can be a dangerous condition that poses serious risks to one’s health and well-being. CGMs offer valuable features that contribute to a safer and more proactive approach to managing glucose levels.
One of the key safety features of CGMs is the ability to set customizable alerts and alarms for glucose levels that fall below or above a specified range. These alerts act as an early warning system, notifying individuals when their glucose levels are approaching or have reached critical thresholds. By receiving timely alerts, individuals can take prompt action to address hypoglycemia before it becomes severe. They can consume glucose-replenishing foods or beverages, adjust their medication, or seek medical assistance as needed. This feature is particularly beneficial for individuals who may experience impaired hypoglycemia awareness, allowing them to avoid potentially dangerous situations.
CGMs also offer retrospective data analysis, allowing individuals to review their glucose trends over an extended period. This feature can be particularly valuable in identifying recurring patterns of hypoglycemia, such as nighttime lows or post-meal drops. Armed with this information, individuals and their healthcare providers can develop targeted strategies to prevent these events, such as adjusting insulin doses, modifying meal timings, or implementing specific safety measures during vulnerable times of the day.
The enhanced safety offered by CGMs extends beyond hypoglycemia prevention. Real-time glucose data also helps individuals recognize and address hyperglycemic episodes promptly. By having a clear view of their glucose levels throughout the day, individuals can take proactive steps to bring their blood sugar within the target range, preventing long-term complications associated with sustained hyperglycemia.
Health Insurance and CGMs
Access to continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) is essential for individuals managing diabetes to benefit from the transformative capabilities of this technology. Health insurance coverage plays a crucial role in ensuring that CGMs are accessible and affordable for those who need them.
Health insurance coverage for CGMs varies among different insurance plans and providers. Coverage for CGMs often requires meeting specific criteria, such as a documented medical necessity and a prescription from a healthcare provider.
Medicare includes coverage for continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) for people who uses insulin. This coverage ensures that eligible individuals have access to this advanced technology. Medicare’s policy on CGM coverage provides detailed information about the eligibility criteria, coverage guidelines, and any additional requirements.

Empowering Self-Management
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) not only improve the present state of diabetes management but also pave the way for empowering self-management and offer exciting future possibilities. These devices enable individuals to take an active role in their diabetes care and provide a glimpse into the potential advancements that lie ahead in diabetes technology.
At Aptiva Medical, we recognize the transformative power of CGMs and are committed to staying at the forefront of this evolving landscape. We are dedicated to exploring the latest advancements in CGM technology and ensuring that our patients have access to the most innovative and effective solutions available. Through continuous research, partnerships with leading manufacturers, and ongoing collaboration with healthcare professionals, we strive to empower individuals with the tools they need to live healthier and more fulfilling lives.
CGMs empower individuals through self-management and open up a world of future possibilities in diabetes technology. By leveraging real-time data, predictive algorithms, and remote monitoring capabilities, CGMs have the potential to revolutionize diabetes management and improve outcomes. As we embrace this technological evolution, we can look forward to a future where individuals with diabetes can lead even more empowered, connected, and healthier lives.