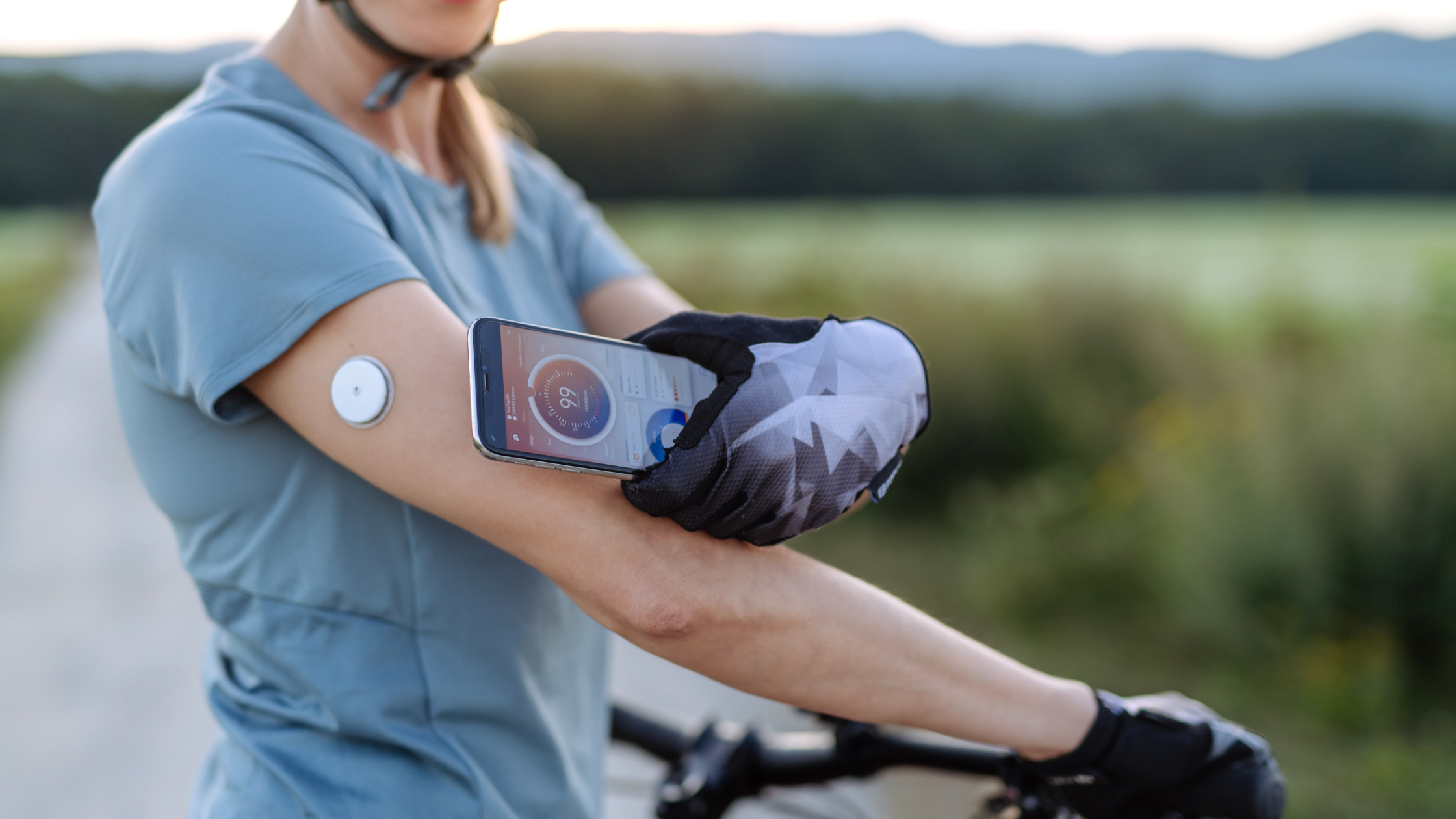
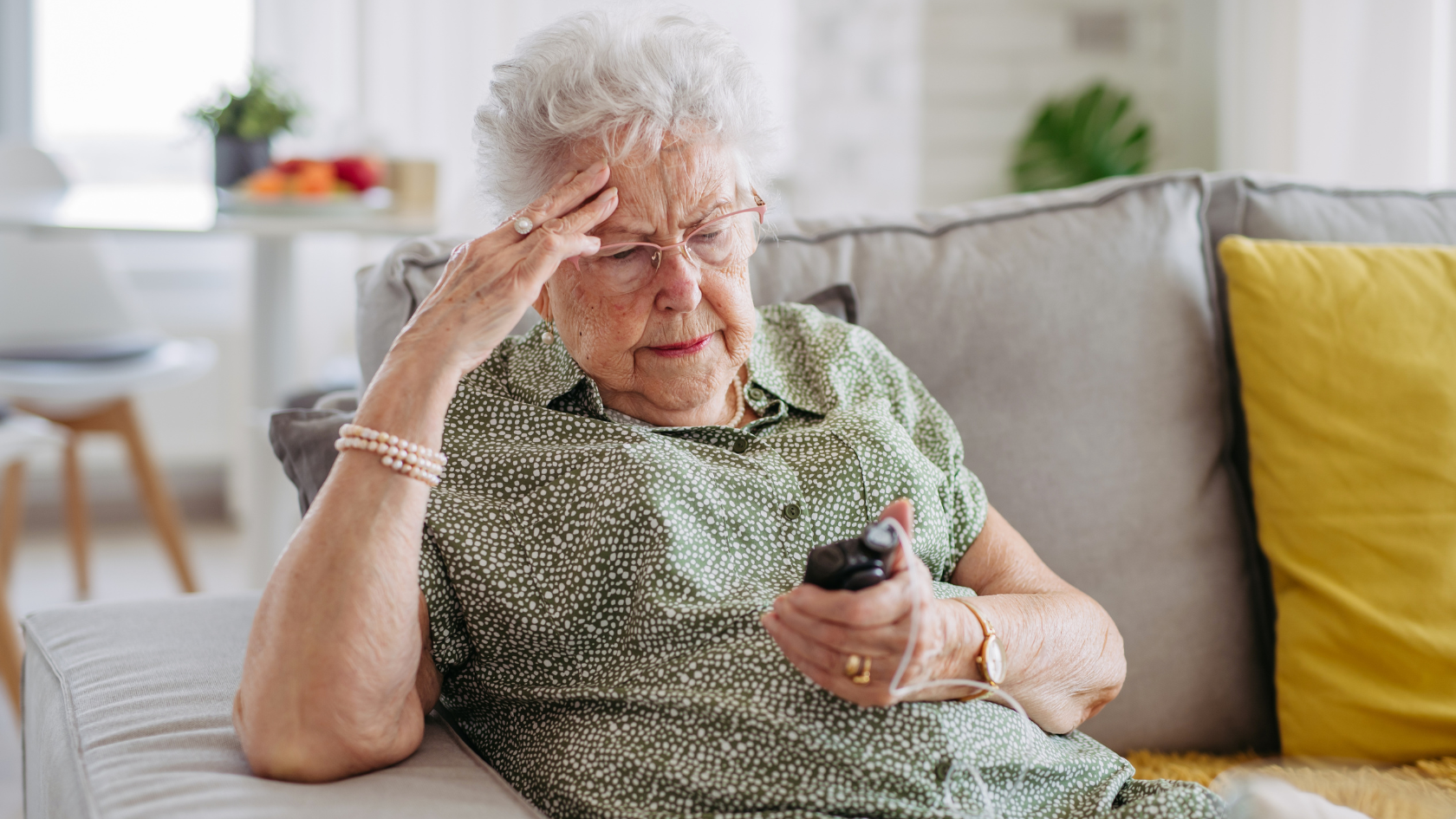
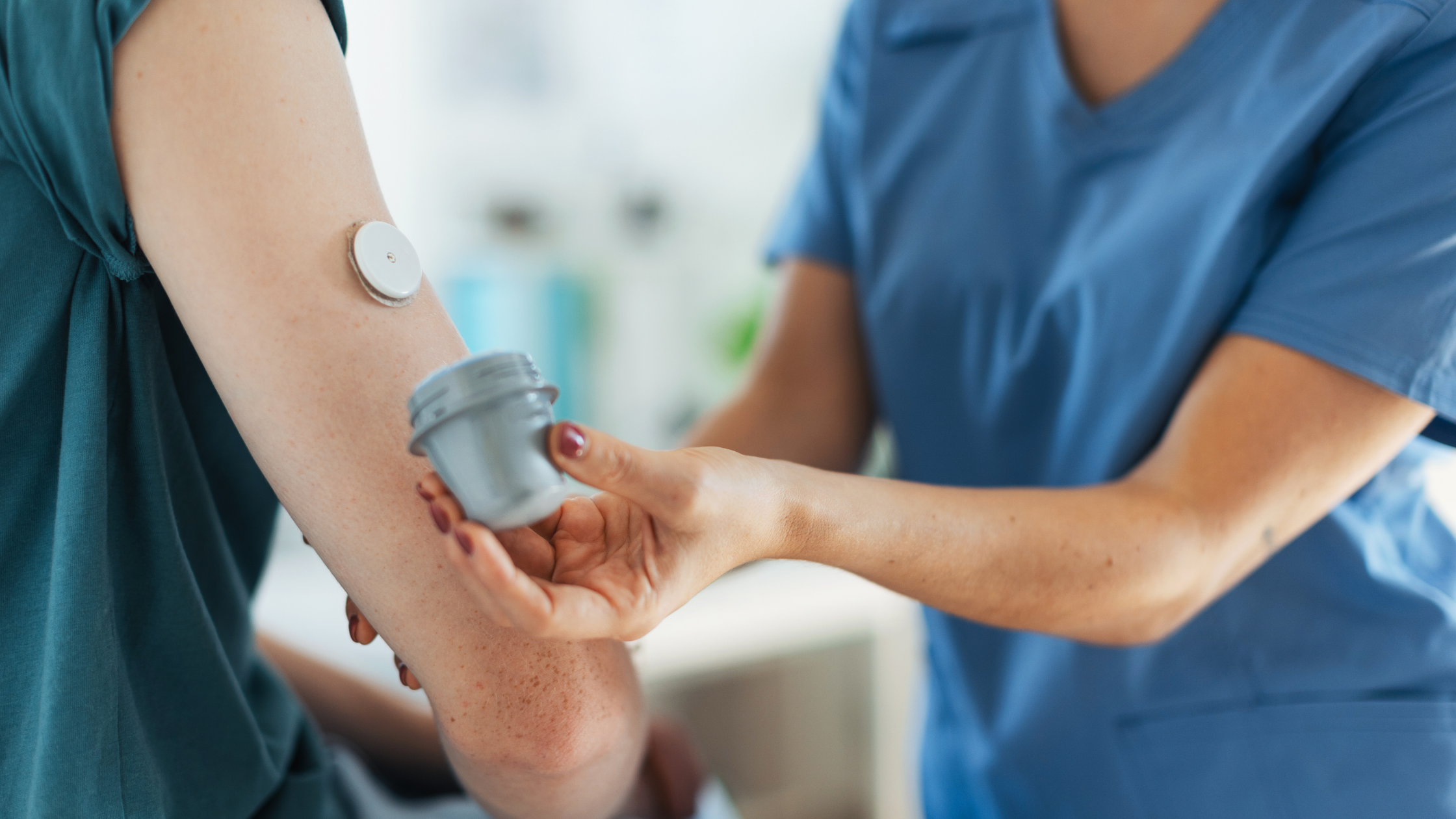
Exercise is a crucial component of managing diabetes, as it helps improve insulin sensitivity, lowers blood sugar levels, and reduces the risk of complications. However, finding the right balance between exercise and glucose control can be challenging. This is where Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) comes into play. CGM devices provide real-time data on glucose levels, enabling individuals with diabetes to make informed decisions about their workouts and optimize their glycemic control.
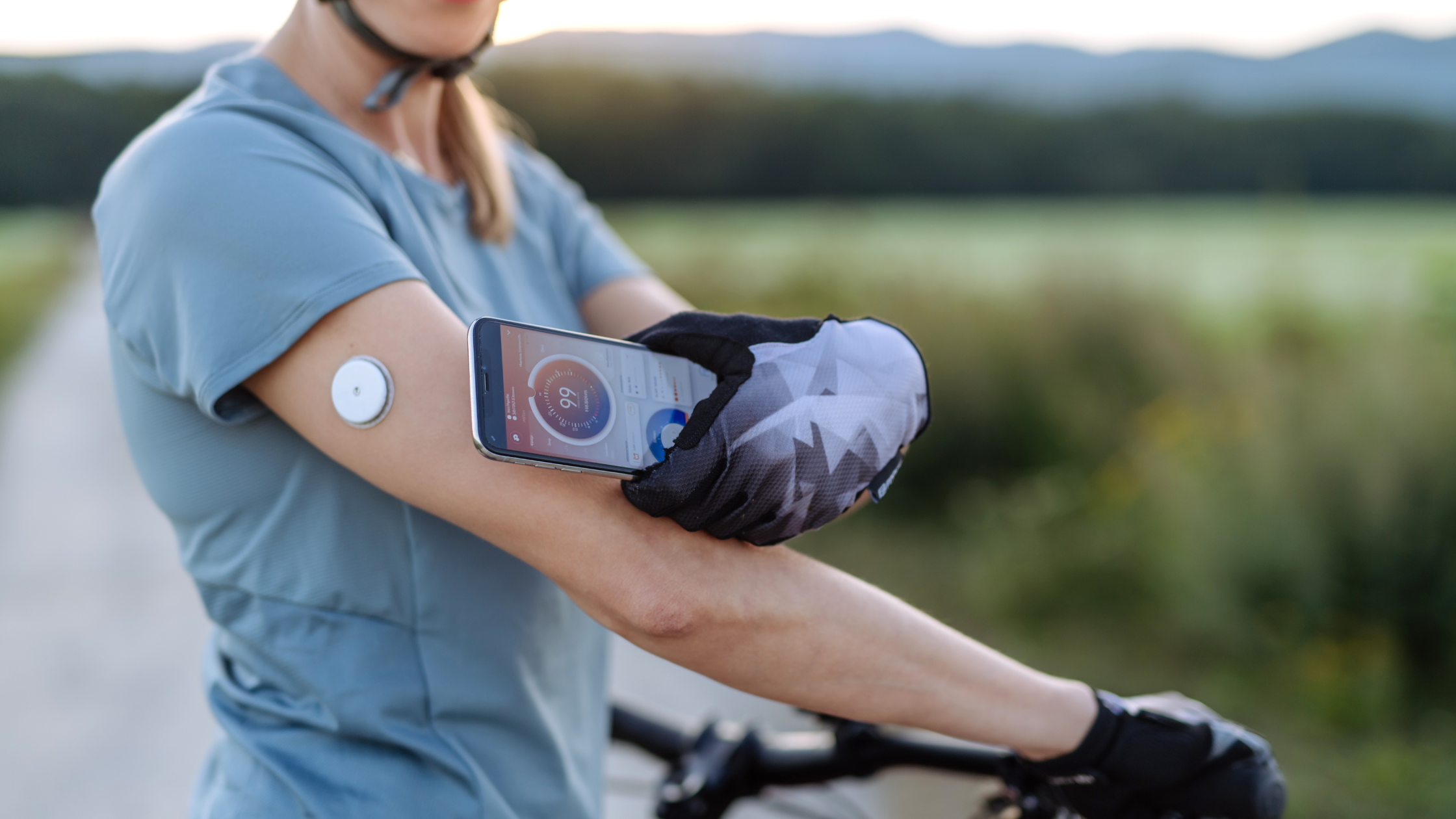

Understanding the Impact of Exercise on Glucose Levels
Different types of exercise and their effects on glucose
Aerobic exercise, such as walking, jogging, cycling, and swimming, has been shown to have a significant impact on lowering blood sugar levels in adults with diabetes. These activities help improve insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to more effectively utilize glucose for energy. Additionally, aerobic exercise promotes the uptake of glucose by the muscles, further contributing to lower blood sugar levels. Engaging in regular aerobic exercise can lead to improved glycemic control and a reduced risk of diabetes-related complications.
Anaerobic exercise, including resistance training and weightlifting, can have a different effect on blood sugar levels compared to aerobic exercise. During high-intensity anaerobic activities, the body releases stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol, which can cause a temporary spike in blood sugar levels. However, in the long run, anaerobic exercise has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and overall glucose control. By increasing muscle mass, resistance training helps the body more efficiently utilize glucose, leading to better glycemic control over time.
However, in the long run, anaerobic exercise has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and overall glucose control. By increasing muscle mass, resistance training helps the body more efficiently utilize glucose, leading to better glycemic control over time.
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT), which involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by periods of rest or low-intensity activity, has gained popularity as an effective way to manage blood sugar levels. HIIT workouts have been shown to rapidly reduce blood sugar levels and improve cardiovascular health in adults with diabetes. The intense nature of HIIT stimulates the body to use glucose more efficiently, leading to improved insulin sensitivity and glycemic control.
However, it is essential for individuals with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels closely when engaging in HIIT and to consult with their healthcare team before starting this type of exercise regimen.
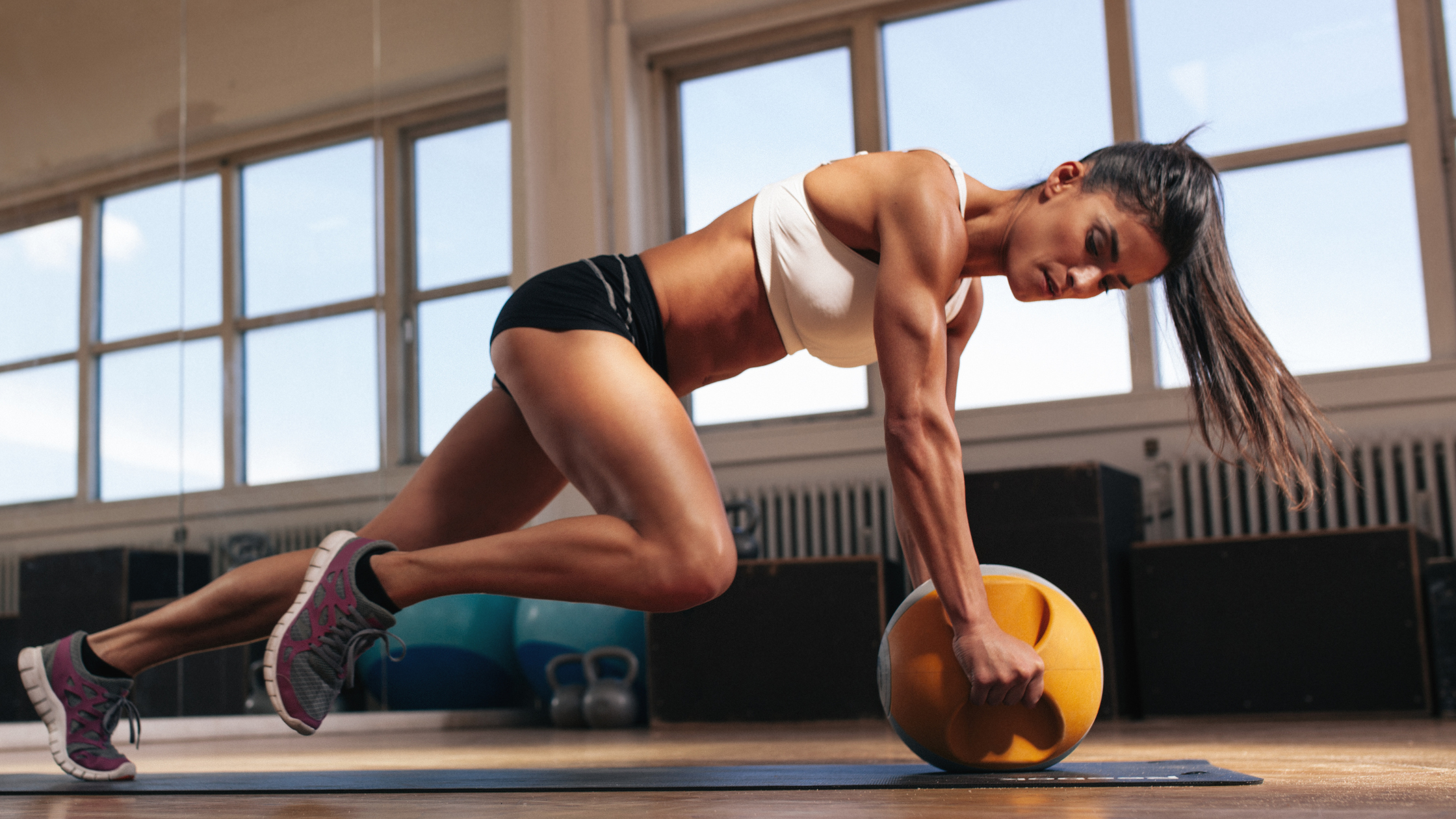

Factors influencing blood sugar response to exercise
Exercise intensity and duration play a significant role in determining an individual’s glucose response to physical activity level. Longer and more intense exercise generally lead to greater reductions in blood sugar levels, as the body requires more glucose to fuel the increased energy demands.
However, it is crucial for individuals with diabetes to strike a balance between exercise intensity and duration to avoid low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) or high blood sugar (hyperglycemia). CGM devices can be particularly useful in monitoring glucose levels during exercise and helping individuals make informed decisions about their workout intensity and duration.
The time of day at which an individual engages in exercise can also influence their glucose response. Some people with diabetes may experience greater insulin sensitivity in the morning, leading to more stable blood sugar levels during and after morning fitness. Others may find that exercising in the afternoon or evening works better for their glycemic control. By using CGM devices to track glucose trends throughout the day, individuals can identify the optimal time for their workouts based on their unique glucose patterns.
By using blood sugar monitoring devices to track glucose trends throughout the day, individuals can identify the optimal time for their fitness based on their unique glucose patterns.
Pre-exercise meals and insulin dosages are critical factors in managing glucose levels during and after exercise. Consuming the right amount of carbohydrates before a workout can help prevent low blood sugar by providing the body with the necessary fuel. However, consuming too many carbohydrates or not adjusting insulin doses accordingly can lead to high blood sugar.
It is essential for individuals with diabetes to work closely with their healthcare team to determine the appropriate pre-exercise meal and insulin adjustments based on the type, intensity, and duration of their planned physical activity. CGM data can provide valuable insights into how different pre-exercise meals and insulin doses affect glucose levels, allowing for more personalized adjustments over time.
Benefits of Using CGM for Exercise Management
Real-time glucose monitoring during workouts
Continuous glucose monitor devices provide continuous, real-time data on glucose levels, allowing individuals to monitor their blood sugar during exercise and make necessary adjustments to prevent hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
Identifying trends and patterns in glucose response to exercise
By analyzing CGM readings, individuals can identify trends and patterns in their glucose response to different types of exercise, helping them tailor their workouts for optimal glycemic control.
Preventing high and low blood sugar during and after exercise
With the insights provided by a continuous glucose monitor, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent low blood sugar or high blood sugar during and after exercise, such as consuming glucose tablets or fruit juice when needed or adjusting insulin doses accordingly.
Customizing Workouts with CGM Data
Analyzing CGM data to optimize exercise plans
Delving into real-time glucose data alongside exercise logs offers a nuanced understanding of how specific activities influence glucose stability. This process not only aids in identifying which workouts best support glycemic stability but also empowers individuals to make evidence-based adjustments to their fitness regimens. Such a personalized approach to exercise planning is grounded in recognizing the unique ways in which one’s body responds to different types of physical activity, leading to more effective diabetes management and overall health improvement.
Adjusting exercise intensity and duration based on glucose trends
Adjusting workout intensity and duration based on glucose monitoring reveals how closely exercise variables align with optimal glucose control. By meticulously analyzing glucose responses to various physical activities, individuals can craft an exercise plan that avoids the extremes of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. This tailored approach not only enhances exercise efficacy but also ensures that physical activities contribute positively to long-term glucose management, enhancing both immediate and future health outcomes.
Modifying pre-exercise meals and insulin doses
Informed by continuous glucose data, individuals can strategically plan their pre-exercise nutrition and insulin dosages to maintain optimal glucose levels during physical activity. This level of customization allows for precise adjustments to dietary intake and insulin administration, mitigating the risk of glucose fluctuations that could impact the effectiveness and safety of exercise. Such adjustments are pivotal in crafting a holistic diabetes management strategy that integrates seamlessly with lifestyle choices, promoting a balanced approach to managing exercise and nutrition.
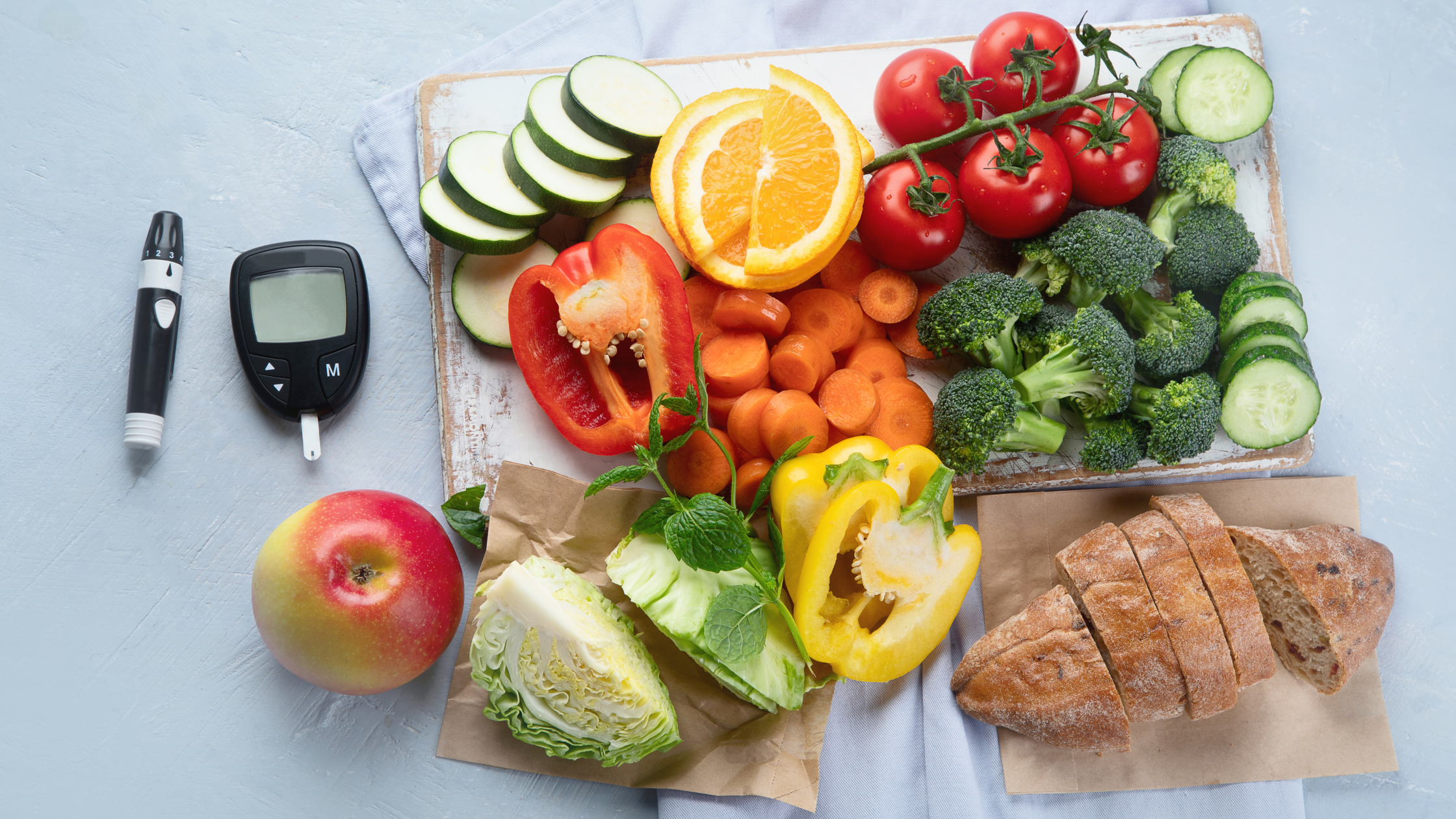

Case studies and examples of successful workout customization
One practical approach to managing glucose levels during exercise involves adjusting carbohydrate intake based on pre-exercise glucose levels. This strategy helps prevent hypoglycemia, especially important during exercise sessions that follow a meal or are performed in a fasting state.
For instance, individuals with pre-exercise blood glucose levels below 90 mg/dL are recommended to ingest 15-30 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates before starting exercise. This tailored approach, facilitated by CGM data, allows for precise adjustments in carbohydrate intake, ensuring that individuals can engage in physical activity safely and effectively.
Moreover, a study conducted by Vanderbilt University Medical Center, which was part of a randomized clinical trials across 15 recruitment centers in the United States, offers an insightful case study relevant to individuals with type 2 diabetes. The study focused on the effectiveness of continuous glucose monitors in managing type 2 diabetes treated with basal or long-acting insulin.
Over eight months, the study followed 175 participants who received their diabetes care from a primary care clinician. It found that using CGMs resulted in significantly lower hemoglobin A1C levels — a test reflecting average blood glucose levels over three months — and better disease management.
Participants using CGMs reduced their A1C by an average of 1.1%, compared to a 0.6% reduction in those using traditional finger-stick glucose monitoring. Moreover, those using CGMs spent, on average, 3.8 more hours per day within the glucose target range, highlighting the practical benefits of CGMs in daily diabetes management.
Tips for Exercising Safely with Diabetes and CGM
Proper hydration and nutrition
When engaging in any form of physical activity, especially for those managing diabetes, it’s crucial to keep your body well-hydrated. Drinking enough water before, during, and after exercise helps your body perform at its best and aids in the recovery process. Similarly, eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, while limiting foods high in saturated fats and sugars, provides the essential nutrients your body needs to function correctly.
For individuals with diabetes, balancing carbohydrate intake with activity levels is particularly important to manage blood sugar levels effectively. Adjusting meal plans and snack choices around workout schedules can help maintain steady blood glucose levels, preventing spikes or drops.
Gradually increasing exercise intensity and duration
Diving headfirst into a new, intense exercise routine might seem like a good idea to achieve quick results, but it can increase the risk of injury or burnout, particularly for those with diabetes. Starting with less intense activities, like walking or gentle yoga, and slowly building up the intensity and duration of workouts allows your body to adjust safely. This gradual approach also provides an opportunity to observe how different types of physical activities affect your blood sugar levels, helping you make more informed decisions about your exercise regimen. Listening to your body and adjusting your workout plans as needed can lead to sustained progress and minimize health risks.
Monitoring glucose before, during, and after workouts
For individuals with diabetes, keeping a close eye on blood sugar levels around exercise times is critical to avoid hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). Using a CGM device can simplify this process by providing real-time glucose readings and alerts if your levels go too high or too low.
This immediate feedback allows for quick adjustments to your activity or nutrition plan, such as consuming a carbohydrate-rich snack if your glucose levels are dropping. Testing your blood sugar before exercise gives you a baseline, while checking during helps you ensure it stays within a safe range. Afterward, monitoring helps assess the impact of the activity on your glucose levels and recovery needs.
Keeping a record of exercise sessions and glucose levels
Documenting your workout routines and corresponding blood sugar readings might seem tedious, but it’s incredibly valuable for long-term diabetes management. This record-keeping helps identify patterns in how different types of exercise impact your glucose levels, enabling you to tailor your physical activity to optimize blood sugar control.
Sharing this log with your healthcare provider can also serve as useful data and improve your care, as it provides them with insights into your daily management and allows for more personalized guidance. Over time, this diary can serve as a motivational tool as well, showcasing your progress and helping you set and achieve new fitness and health goals.
How Aptiva Supports Exercise Management with CGM
Overview of our CGM devices and their features
Continuous glucose monitoring devices offer significant advantages over traditional blood glucose monitoring methods, such as fingerstick tests. They provide continuous, real-time glucose readings, allowing for immediate adjustments to diet, exercise, and medication. This can help prevent both high and low blood sugar levels. Unlike traditional methods, CGMs offer a more comprehensive picture of glucose trends throughout the day and night, enabling better diabetes management. They also reduce the need for frequent finger pricks, making glucose monitoring less invasive and more convenient for users.
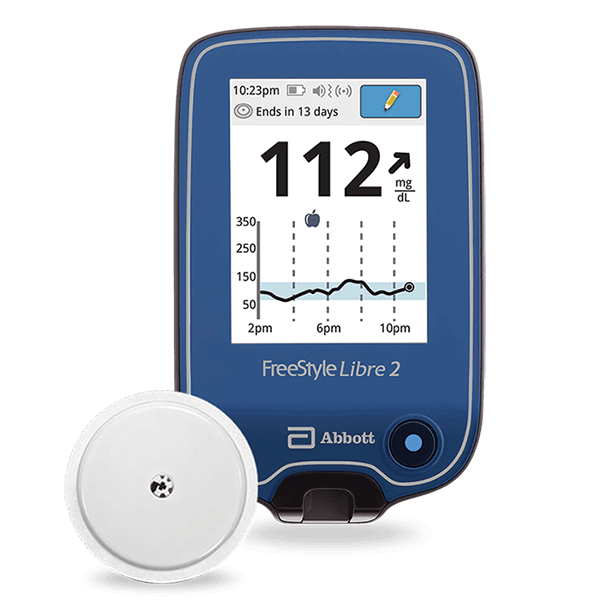
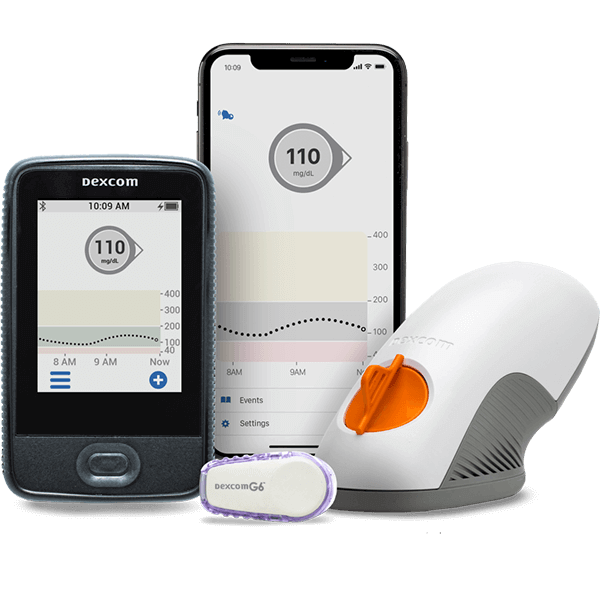
Aptiva Medical offers a variety of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems designed to meet the needs of individuals with diabetes. These devices provide real-time insights into glucose levels, helping users make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication.
The CGM devices available include the FreeStyle Libre and Dexcom, each offering unique features to support diabetes management. These systems are designed for ease of use, providing continuous glucose data to a standalone reader or a smartphone app, with sensor wear times ranging from 10 to 14 days.
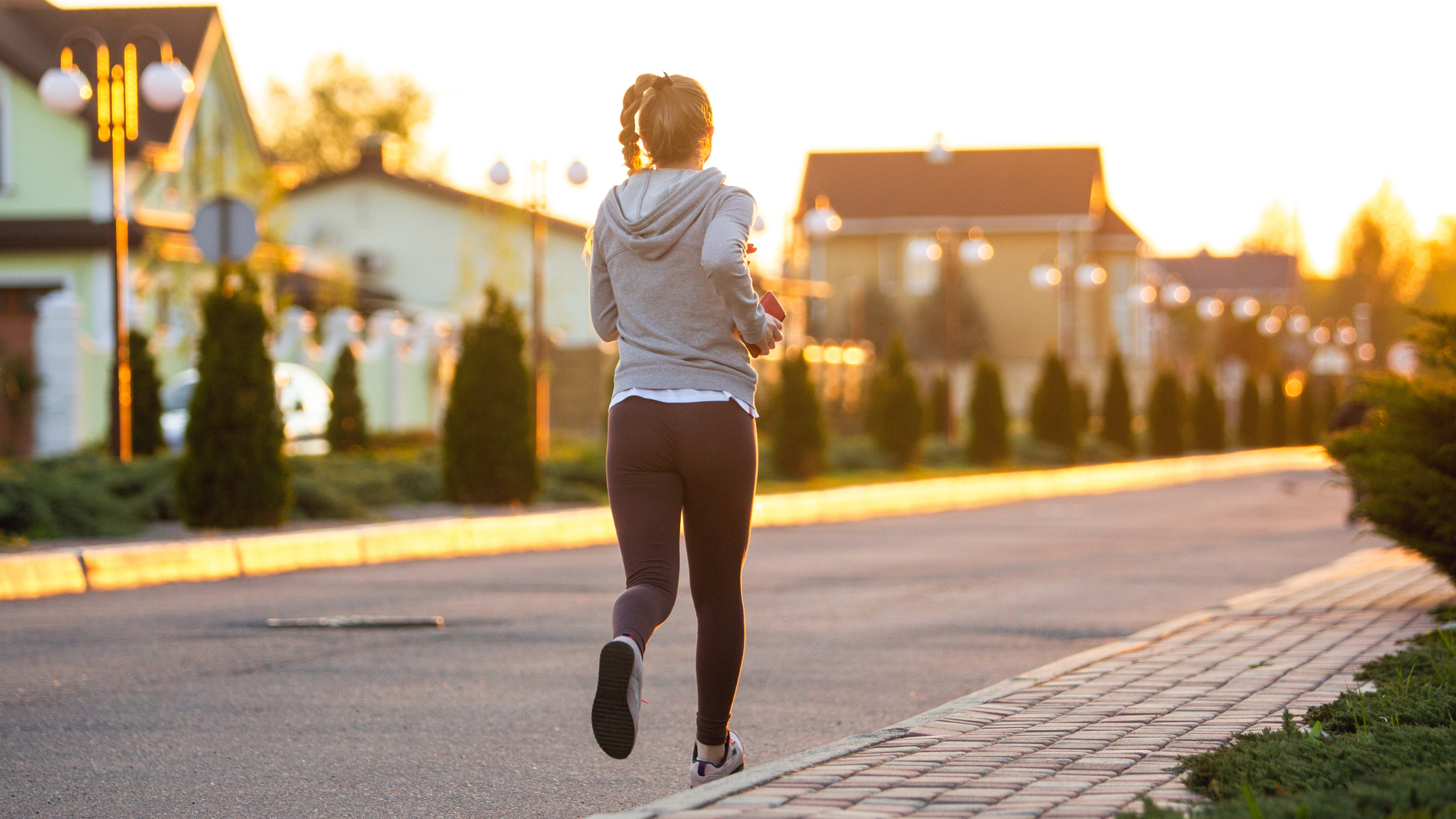

Integration with fitness apps and wearables
Our CGM devices seamlessly integrate with popular fitness apps and wearables, allowing patients to easily track their workouts alongside their glucose data for a holistic view of their health.
Conclusion
Incorporating CGM into exercise management can be a game-changer for individuals with diabetes, providing real-time insights into glucose trends and enabling personalized workout plans for better glucose control. By utilizing CGM data to customize exercise intensity, duration, and pre-workout nutrition, individuals can safely engage in physical activity and reap the numerous health benefits it offers.
We encourage readers to work closely with their healthcare provider and explore how CGM can support their exercise goals. To learn more about our company’s cutting-edge CGM solutions and how they can help you optimize your workouts and glycemic control, visit our website or reach out to our knowledgeable staff.
By harnessing the power of CGM and tailoring exercise plans accordingly, individuals with diabetes can take control of their health conditions, reduce the risk of complications, and lead fuller, more active lives. Let us help you on this journey towards better disease control and improved overall well-being.