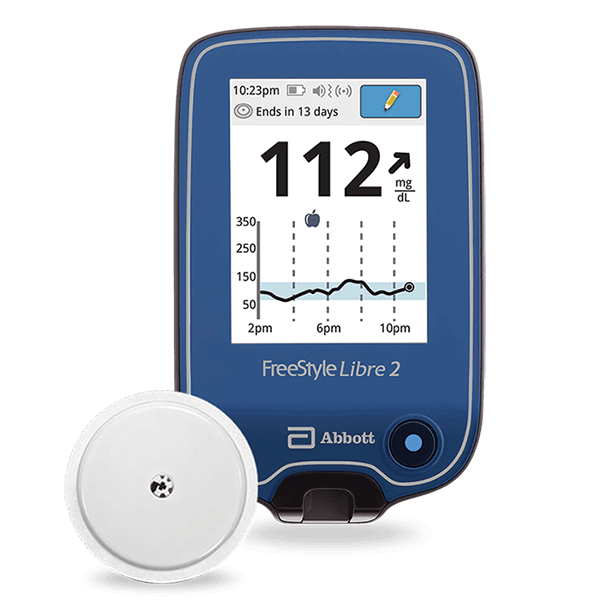
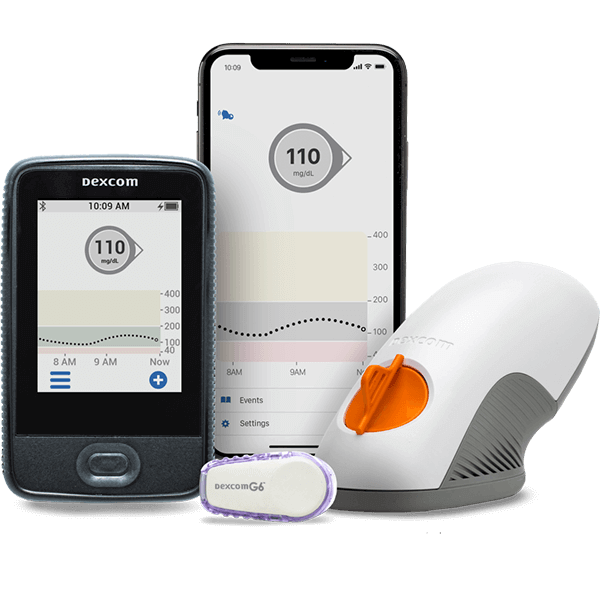
Managing your blood sugar levels is crucial in controlling diabetes, and one critical metric to measure your blood sugar control is “Time in Range” (TIR). TIR refers to the percentage of time you spend within a target blood glucose range, typically set by your healthcare provider, and it is a valuable indicator of how well you are managing your diabetes and overall health outcomes.
Having a higher TIR means that your blood sugar levels are consistently within your target range, which is associated with better diabetes management and reduced risk of complications. On the other hand, a lower TIR indicates that your blood sugar levels may be frequently outside of the target range, which may lead to an increased risk of short-term and long-term diabetes complications.
In this article, we will explore practical tips and tricks to help you improve your TIR and effectively manage and maintain your average blood glucose levels.

Understanding Time in Range (TIR)
You can measure TIR by calculating the percentage of time you spend within a target blood glucose range. It provides insights into how well your blood glucose levels are staying within a desired range over a specific period of time, typically a day or a week. TIR is considered a principal metric for diabetes management because it offers a more comprehensive picture of your blood glucose control compared to traditional measures such as HbA1c, which provides an average blood glucose level over a longer period of time.
This makes the A1c a measure that can be influenced by various external factors. As such, many are leaning towards the simplicity of TIR. The higher the time in the range percentage, the lower the risk of developing complications. The lower the TIR, the higher the glucose variability and thus the risk of possible complications. Another great thing about the Time in Range value is that you can figure it out yourself! If you are a user of a continuous glucose monitoring at home, you do not have to go to a doctor or to a laboratory as you would with the HbA1c value.
Maintaining your blood glucose levels within a target range is valuable in reducing the risk of both hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) complications. Hypoglycemia can cause symptoms such as dizziness, confusion, and even loss of consciousness, while hyperglycemia can lead to long-term complications such as nerve damage, chronic kidney disease, and cardiovascular problems.
Time in range target on CGM systems
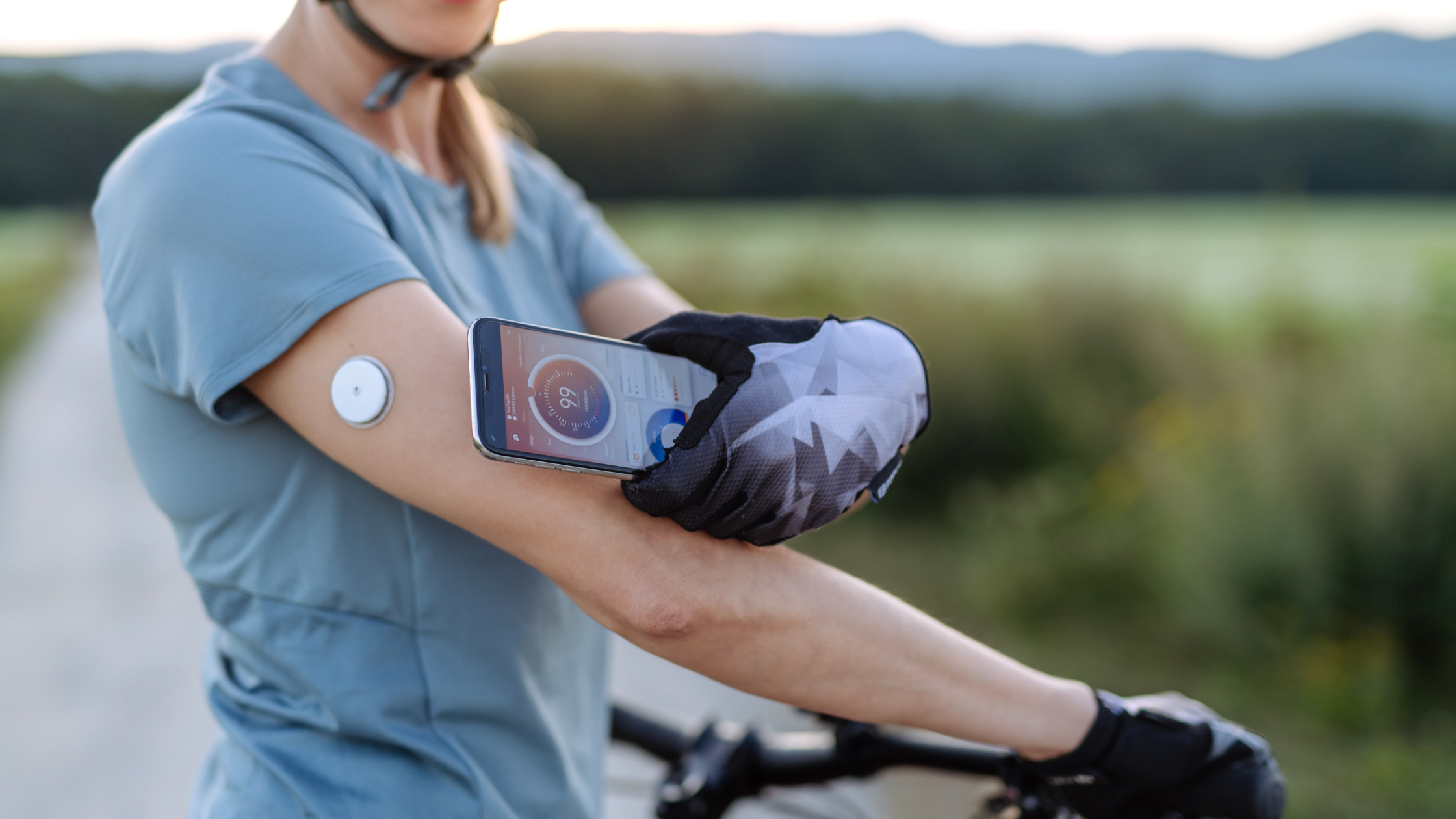
Using Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems can be a valuable tool in improving Time in Range for individuals with diabetes. CGM systems involve wearing a small sensor under the skin that measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid throughout the day and night, providing real-time data on blood sugar fluctuations and helping evaluate blood glucose control.
The importance of CGM in improving TIR lies in its ability to pro vide detailed and continuous information about blood glucose levels and TIR data, allowing for timely adjustments to diabetes management strategies.
As for what time in range target you should aim for, remember: there’s no universal time in range goal. For instance, individuals who are pregnant or have complications like retinopathy may require a narrower range to minimize risks. Conversely, those who frequently experience hypoglycemia may need a wider range to reduce the risk of low blood sugar episodes. Yours will depend on your diabetes management needs and lifestyle, and your doctor can help you determine the right range for you.
The recommended TIR targets may vary depending on factors such as your age, diabetes type, and overall health condition. Generally speaking, the clinical target time in range for FreeStyle Libre 2, Dexcom G6, and other continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems typically aims for a TIR of 70-180 mg/dL, which means that your blood glucose value is within this range for a significant portion of the day.
Tips for Improving Your Time in Range
Monitor your blood glucose regularly and consistently
Regular and consistent blood glucose monitoring is critical for effective diabetes management. By using CGM systems, you can monitor your blood glucose levels regularly and obtain real-time data and insights.
It’s essential to follow the monitoring frequency recommended by your healthcare provider and keep a log or journal of your blood glucose readings to track trends. Discussing your continuous glucose monitoring data with medical experts can help you develop better management strategies tailored to your needs.

Understand and interpret CGM data
Using a CGM system can simplify blood glucose monitoring, but it’s essential for you to understand how to interpret the data it provides. Interpreting blood glucose data is vital in identifying patterns and making informed decisions about your diabetes management. Regularly review your CGM data, paying attention to parameters such as time in target range, time below target range (hypoglycemia), and time above target range (hyperglycemia).
Look for patterns or trends in your data, such as recurring high or low blood glucose levels at specific times of the day or after certain meals. Discuss the patterns you observe with your doctor to optimize your blood glucose control and improve your overall diabetes management.

Follow a healthy and balanced meal plan
Make sure to follow a healthy and balanced meal plan for effective blood glucose management. Collaborate with a registered dietitian or nutritionist to develop a meal plan that includes a variety of foods from all food groups in appropriate portions.
Opt for complex carbohydrates like whole grains, legumes, and vegetables instead of simple carbohydrates found in sugary beverages and sweets.
Incorporate lean proteins such as poultry, fish, beans, and tofu to help stabilize blood glucose levels.
Avoid excessive consumption of high-sugar and high-fat foods as they can cause blood glucose spikes and negatively impact your Time in Range.
By making healthy food choices and following a balanced meal plan, you can optimize your blood glucose management and overall diabetes care.

Engage in regular physical activity
Regular exercise can play a crucial role in improving blood glucose control and Time in Range (TIR). Aim for a combination of aerobic exercises, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, and strength training exercises like weight lifting or resistance bands for optimal benefits.
Monitoring your blood glucose levels before, during, and after exercise is essential to understand how it affects your blood sugar levels and make necessary adjustments to prevent hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
It’s also critical to stay hydrated during exercise and carry a source of fast-acting glucose, such as glucose tablets or juice, in case of a low blood sugar episode. By being mindful of your blood glucose levels and making necessary adjustments, regular exercise can be a beneficial component of your overall diabetes management plan.
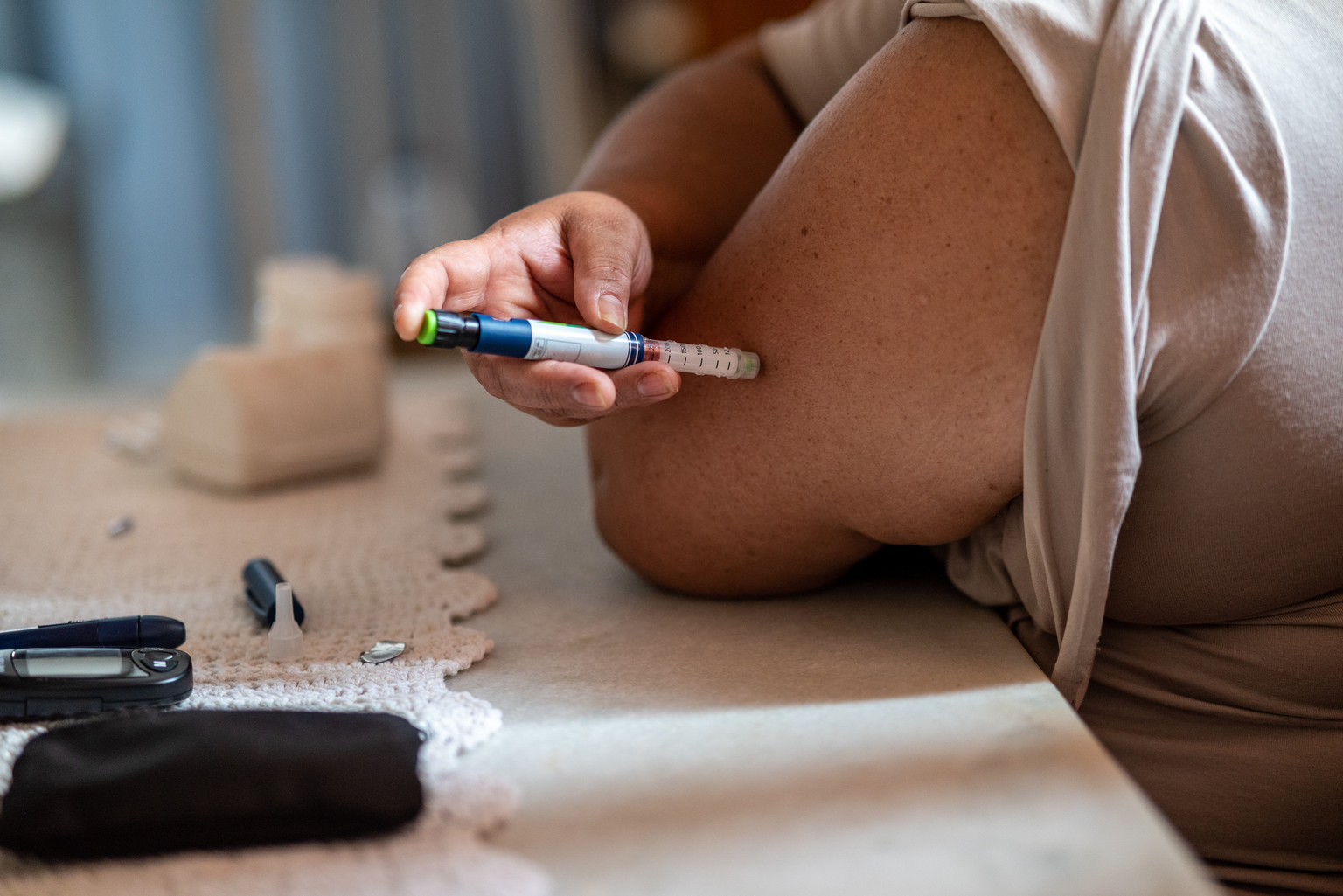

Adhere to your medication and insulin regimen
Medications and insulin are vital components in effectively managing blood glucose levels. It’s crucial to take your medications or insulin as prescribed by your health professional and adhere to the recommended dosages and timing.
If you are on insulin therapy, work closely with your healthcare provider to fine-tune your insulin regimen based on your blood glucose data and lifestyle changes. When making changes to your medication or insulin regimen, be vigilant about monitoring your blood glucose levels to understand their impact on your Time in Range (TIR).
Additionally, inform your doctor about any changes in your health, lifestyle, or medications that may affect your blood glucose control, and work together to make necessary adjustments. By closely following your doctor’s guidance and being proactive in monitoring and communicating changes, you can optimize the effectiveness of your medication or insulin regimen in managing your blood glucose levels.
Challenges and Solutions for Improving Time in Range
Achieving and maintaining TIR, which refers to the percentage of time spent within the target blood glucose range, can be challenging for individuals with diabetes. Various factors, including emotional aspects, social situations, time management, and financial considerations, can pose barriers to consistently maintaining optimal blood glucose levels. However, with awareness and proactive strategies, these challenges can be overcome.

Emotional aspects
Stress, anxiety, and depression, can impact blood glucose management. Stress hormones can raise blood glucose levels, while mental health conditions may affect motivation and self-care behaviors. To address emotional challenges, it’s important to prioritize self-care, practice stress management techniques, seek support from healthcare providers, counselors, or support groups, and communicate openly with loved ones about your emotional well-being.
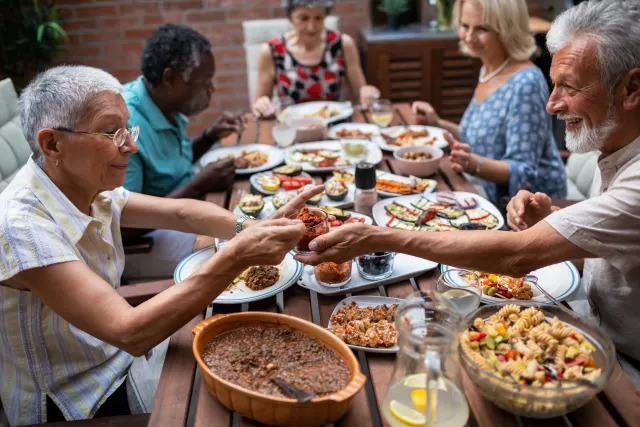

Social situations
Dining out, attending social events, or traveling, can pose challenges in managing blood glucose levels. Peer pressure, lack of control over food options, and disruptions in routine may impact blood glucose control. Planning ahead and being proactive can help overcome these challenges. Strategies may include researching restaurant menus in advance, bringing healthy snacks, staying hydrated, and being assertive in declining foods that may adversely impact blood glucose levels. Additionally, open communication with friends, family, and social circles can foster understanding and support.

Time management
Organizing one’s time can also be a challenge in blood glucose management. Balancing work, family, and other responsibilities may lead to neglecting self-care tasks, such as monitoring blood glucose levels, exercising, or meal planning. Setting priorities, creating a schedule, and utilizing reminders or alarms can help in managing time effectively. Incorporating self-care tasks into daily routines and involving family members or caregivers for support can also be beneficial.
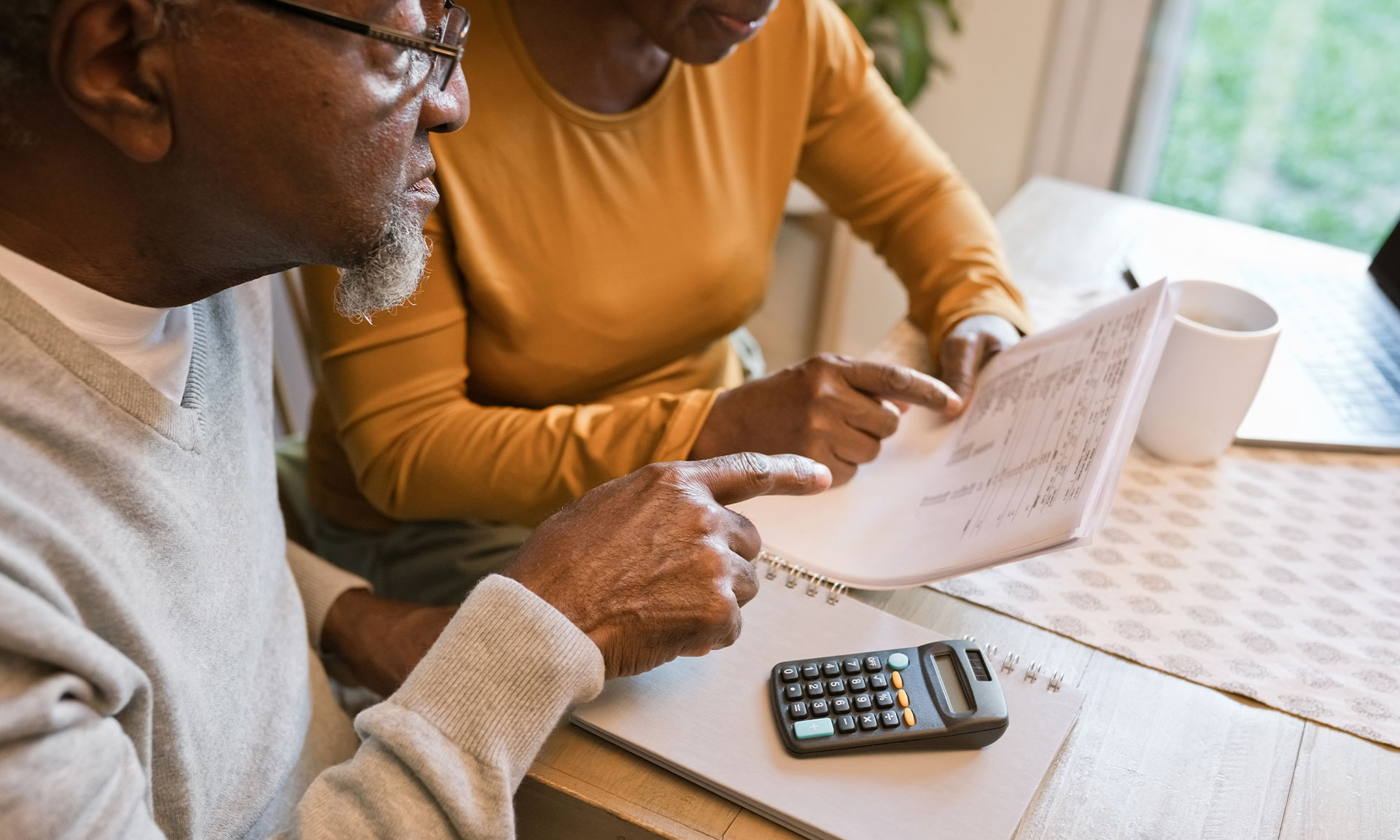

Financial considerations
Things like the cost of medications, supplies, and diabetes management tools, can be a barrier to optimal blood glucose control. It may be challenging to afford continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices, insulin pumps, or regular medical appointments. However, there are potential solutions, such as working with healthcare providers to explore cost-effective options, utilizing insurance benefits, accessing patient assistance programs, and seeking community resources for financial support. Order through Aptiva Medical to find out if you qualify for full coverage. Then you can choose the CGM system you want with the help of a knowledgeable support agent. Once you decide, Aptiva works with your insurance company and delivers to your door at no cost to you.
Managing blood glucose levels and achieving Time in Range (TIR) is crucial for individuals with diabetes to reduce the risk of complications associated with hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.
Regular blood glucose monitoring, understanding and interpreting CGM, following a healthy meal plan, engaging in regular physical activity, adhering to medication regimens, managing stress, and collaborating with healthcare providers are practical tips and tricks that can help improve TIR and effectively manage blood sugar levels for better health outcomes.
Despite challenges, solutions such as managing emotional aspects, seeking social support, making lifestyle changes, adjusting medications, and utilizing technology can help individuals with diabetes overcome challenges and improve TIR.
Note: It’s important to work closely with healthcare providers and other members of the diabetes care team to develop personalized strategies for blood glucose management and achieve optimal Time in Range. Being able to know your average blood glucose levels as well as the highs and lows time in range provides a bigger picture of what’s needed to manage your diabetes.